Strengthening of Hat section trusses under heavy loads
Scottsdale pioneers in the cold-formed roof and floor truss technology and are the trusted partners in the industry to offer cutting edge solutions for prefabricated construction. We offer two profiles such as Hat and Cee sections for manufacturing these trusses. The Cee section trusses are fabricated in-line about the weaker minor axis of the sections while the Hat section trusses are fabricated about the strong major axis of the section.
Hat section trusses oriented about the major axis offers significant advantages in comparison to the Cee section trusses about the minor axis. Some advantages include greater strength to weight ratio, more spans, stronger connections through bolts, easier fabrication and robust performance during erection and service lifetime.
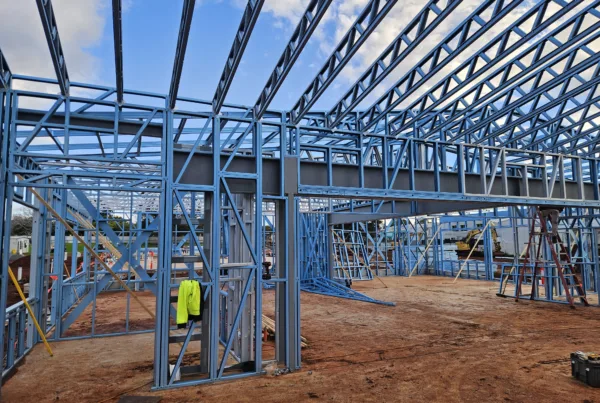
 Typical house construction with Scottsdale Hat section roof trusses
Typical house construction with Scottsdale Hat section roof trusses
Typical floor joist with Scottsdale Hat sections
Despite the orientation of the members about the strong major axis, there can be instances where the hat section truss member fails due to extreme loading conditions
These limitations are often addressed in the design by either of the following:
- Decreasing the truss spacing
- Choosing a higher thickness/gauge
- Decreasing the truss span by introducing additional bearing points on the wall
- Increasing the connection capacity by introducing additional screw fasteners on top of the bolted connection
- Revisiting the assumptions to the loads applied on to the trusses
Despite these mitigation efforts, there can still be instances where the truss chord and web members fail the engineering checks. These failures are often attributed to excessive load demands on these members exceeding the design capacities. This article summarises some methodologies to overcome these design failures for Hat section trusses and provide optimal solutions for the cold-formed steel truss designers.
Web braces between chord members
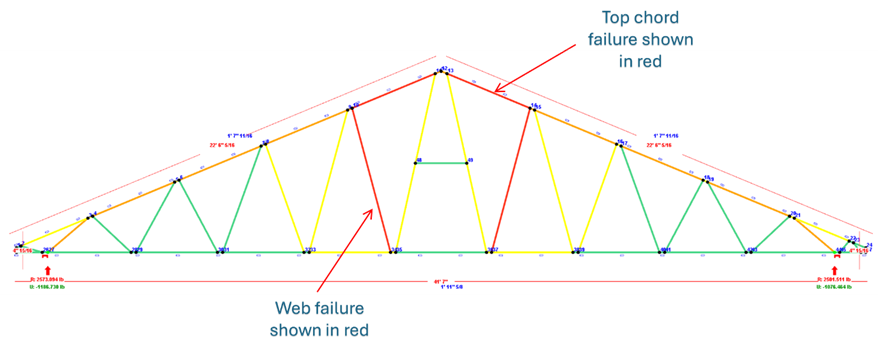
Chord members are those that are mostly affected by the application of heavy loads in a truss as they act as the first point of contact to transfer the loads. Subsequently, the web members take the excessive load thereby failing the engineering design checks as shown below.
Image showing truss chord members failing – No web braces
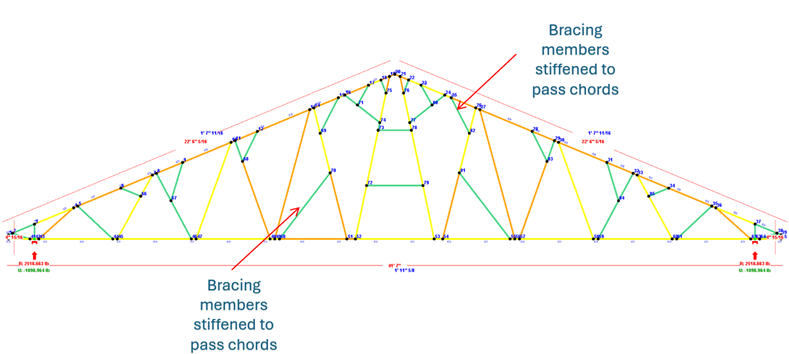
Image showing truss members passing with web brace strengthening
To overcome such failures within ScotSteel, the truss is made 2 Ply to pass engineering. However, this adds additional steel usage resulting in uneconomical solution. Alternatively, web braces can be introduced in strategic locations as shown in image above to make the truss members to pass the engineering checks as per the respective country code of practice. This technique can be used in a wide variety of situations in both roof and floor trusses to strengthen the failing members. The web member failure can also be strengthened by the addition of back-to-back sections as well. ScotSteel can insert these web braces at any given angle through the use of the following options and can also engineer these strengthening options automatically for various country codes.
Toolbar items to include web braces for strengthening
Chord strengthening through truss insert
The truss machines have the ability to cope the hat section flanges thereby resulting in unlipped hat section. To strengthen the failed top and bottom chord members, these coped sections can be inserted into the chord members thereby increasing the strength of these chord members. Typical section view of the chord member strengthening through truss insert is shown below:
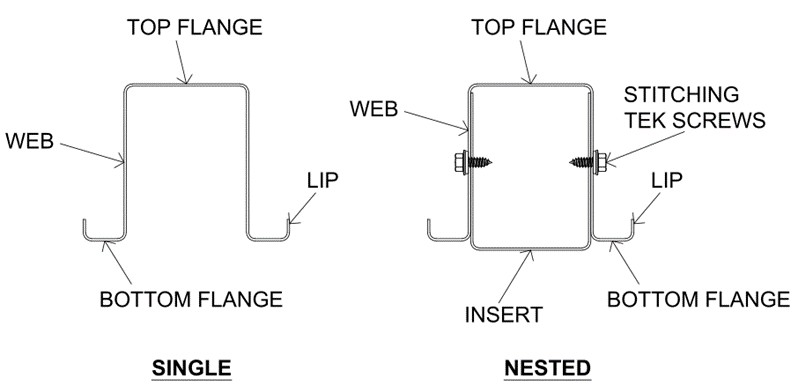
Image showing single and nested sections
Connections between the truss insert with the chord members can be done through tek screws at 300 mm interval as shown in the section view above. Table below summarises the CSI ratio up to which these truss inserts can be used to strengthen the chord members.
| Overstress CSI ratio – Member only | Insert | Fixity |
| <1 |
Member passes. No strengthening needed |
Not applicable |
| >1<=1.3 | Insert of a similar thickness |
Tek screw on wither side at 300 mm c-c |
| >1.3 |
Opt for a stronger section |
Opt for a stronger connection |
It is to note that strengthening of the web members is advisable to be done through back-to-back arrangement of the hat section. Web members within a truss experience axial compression/tensile forces induced on them. The axial load carrying capacity of the back-to-back section exceeds that of the nested section resulting in better performance.
ScotSteel does not have the ability to engineer these strengthening options automatically, but these strengthening options can be used in consultation with the certifying engineer.
Contact us
Feel free to reach out to us for utilising these truss strengthening options within your project to get the maximum benefit out of the Cee section trusses.
Inquire today at 1 (888) 406-2080 or sales@scottsdalesteelframes.com